| Namespace | http://diggsml.org/schemas/3 | |||||||||||||||||
|
Annotations
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
Diagram
|
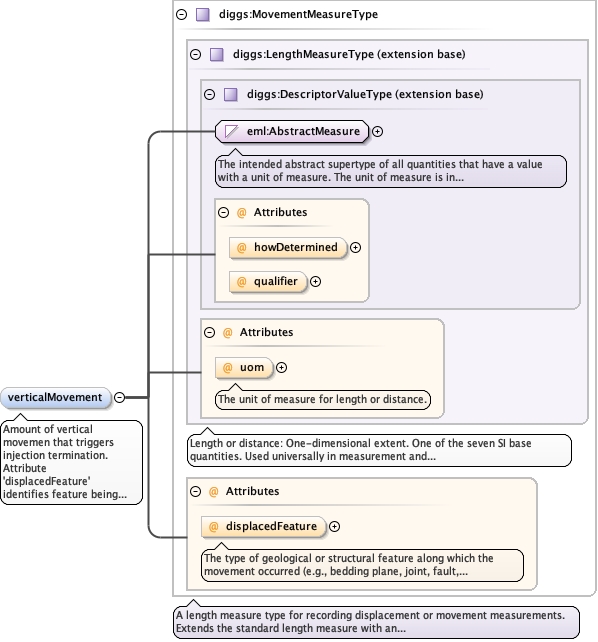
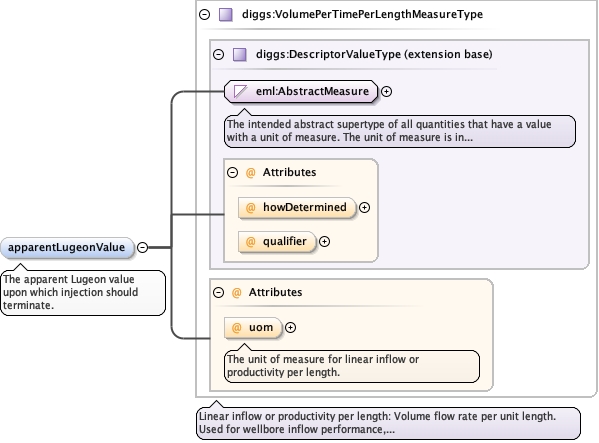 |
|||||||||||||||||
| Type | diggs:VolumePerTimePerLengthMeasureType | |||||||||||||||||
| Type hierarchy | ||||||||||||||||||
|
Properties
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
Attributes
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
| Schema location | file:/Users/dponti/GitHub/diggs-schema/specialty/Grouting.xsd |