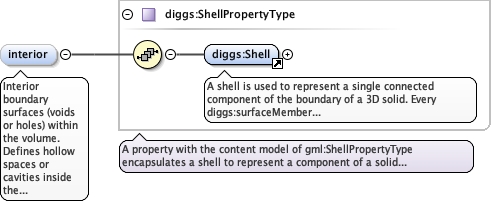
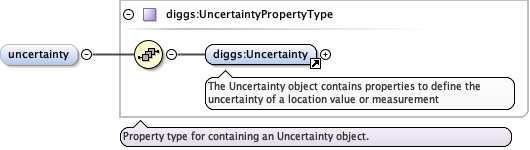
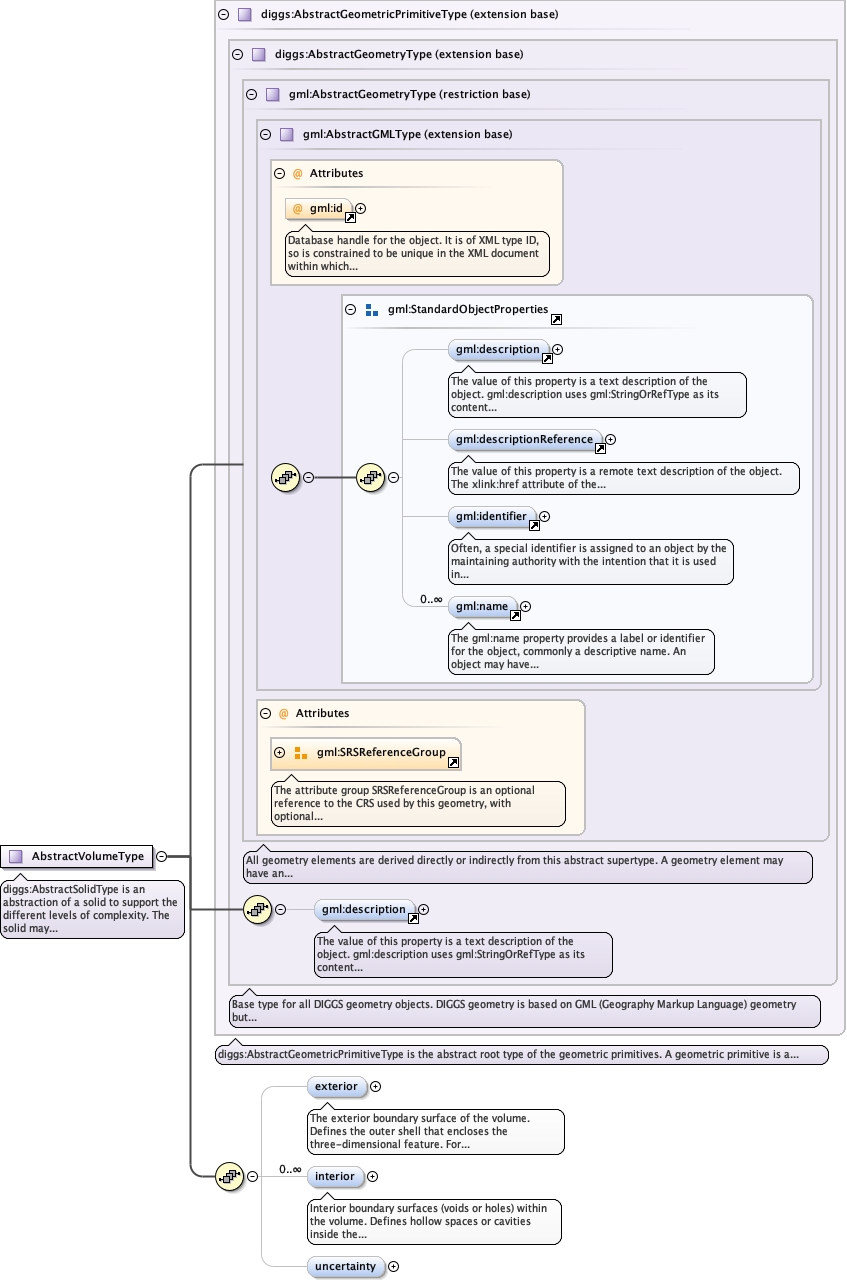
| Namespace | http://diggsml.org/schemas/3 | ||||
|
Annotations
|
|
||||
|
Diagram
|
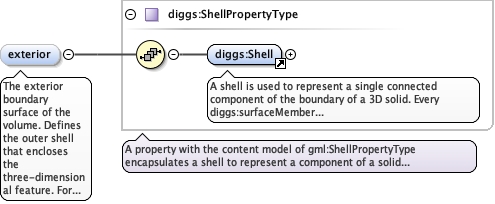 |
||||
| Type | diggs:ShellPropertyType | ||||
|
Properties
|
|
||||
| Model | |||||
| Children | diggs:Shell | ||||
|
Instance
|
|
||||
| Schema location | file:/Users/dponti/GitHub/diggs-schema/extended/ExtSamplingFeatures.xsd |