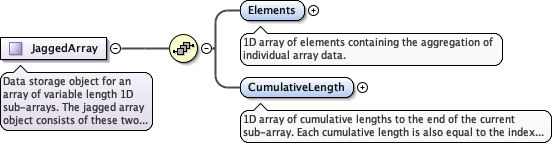
<xs:complexType name="JaggedArray">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>Data storage object for an array of variable length 1D sub-arrays. The jagged array object consists of these two arrays: - An aggregation of all the variable length sub-arrays into a single 1D array. - The offsets into the single 1D array, given by the sum of all the sub-array lengths up to and including the current sub-array. Often referred to as a "list-of-lists" or "array-of-arrays" construction. For example to store the following three arrays as a jagged array: (a b c) (d e f g) (h) Elements = (a b c d e f g h) Cumulative Length = (3 7 8)</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
<xs:sequence>
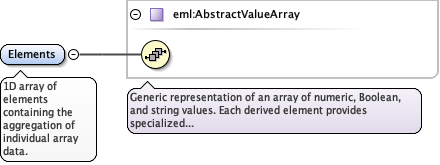
<xs:element name="Elements" type="eml:AbstractValueArray" minOccurs="1" maxOccurs="1">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>1D array of elements containing the aggregation of individual array data.</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:element>
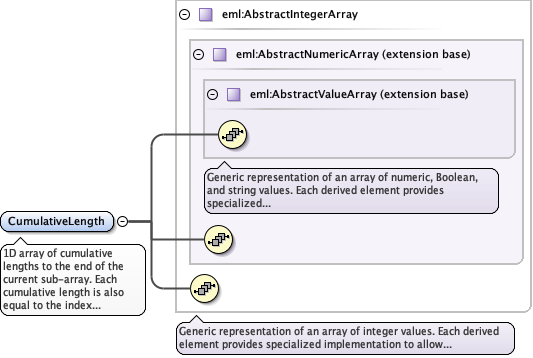
<xs:element name="CumulativeLength" type="eml:AbstractIntegerArray" minOccurs="1" maxOccurs="1">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>1D array of cumulative lengths to the end of the current sub-array. Each cumulative length is also equal to the index of the first element of the next sub-array, i.e., the index in the elements array for which the next variable length sub-array begins.</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:element>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
|